Cross-Chain
Axiomesh’s cross-chain mechanism is applicable to all EVM-compatible blockchains. It not only ensures the transmission of cross-chain messages but also guarantees transaction integrity when Axiomesh interacts with other chains or when other chains interact with Axiomesh for asset exchanges.
Cross-Chain Relayer
The cross-chain relayer is a crucial component within Axiomesh’s cross-chain system. Its primary function is to relay cross-chain messages from one chain to another. The cross-chain relayer consists of two parts with different roles. Only when both parts are committed can the cross-chain message be effectively executed on the target chain. This mechanism prevents the malicious behavior from a single point.
Axiomesh has its own officially maintained cross-chain relayers. We recommends users or applications to use the official cross-chain relayers to ensure the security of asset cross-chain operations and the accuracy of messages.
Cross-Chain Manager Contracts
The cross-chain management contract serves as the engine within Axiomesh’s cross-chain system. When a user or an on-chain application initiates a blockchain cross-chain request, it must go through the cross-chain management contract.
The source chain’s cross-chain management contract encompasses the management of cross-chain entities, routing for cross-chain types, encapsulation of cross-chain messages, and the propagation of cross-chain events.
The cross-chain management contract on the destination chain includes checks for the target of cross-chain messages, decoding of encapsulated cross-chain messages, and invocation of the destination contract.
Cross-Chain Process
Message Cross-Chain Process
Cross-chain message delivery is relatively straightforward. Users and applications only need to send the message they want to deliver to the cross-chain management contract. Axiomesh’s cross-chain system will then relay the message to the corresponding contract on the destination chain.
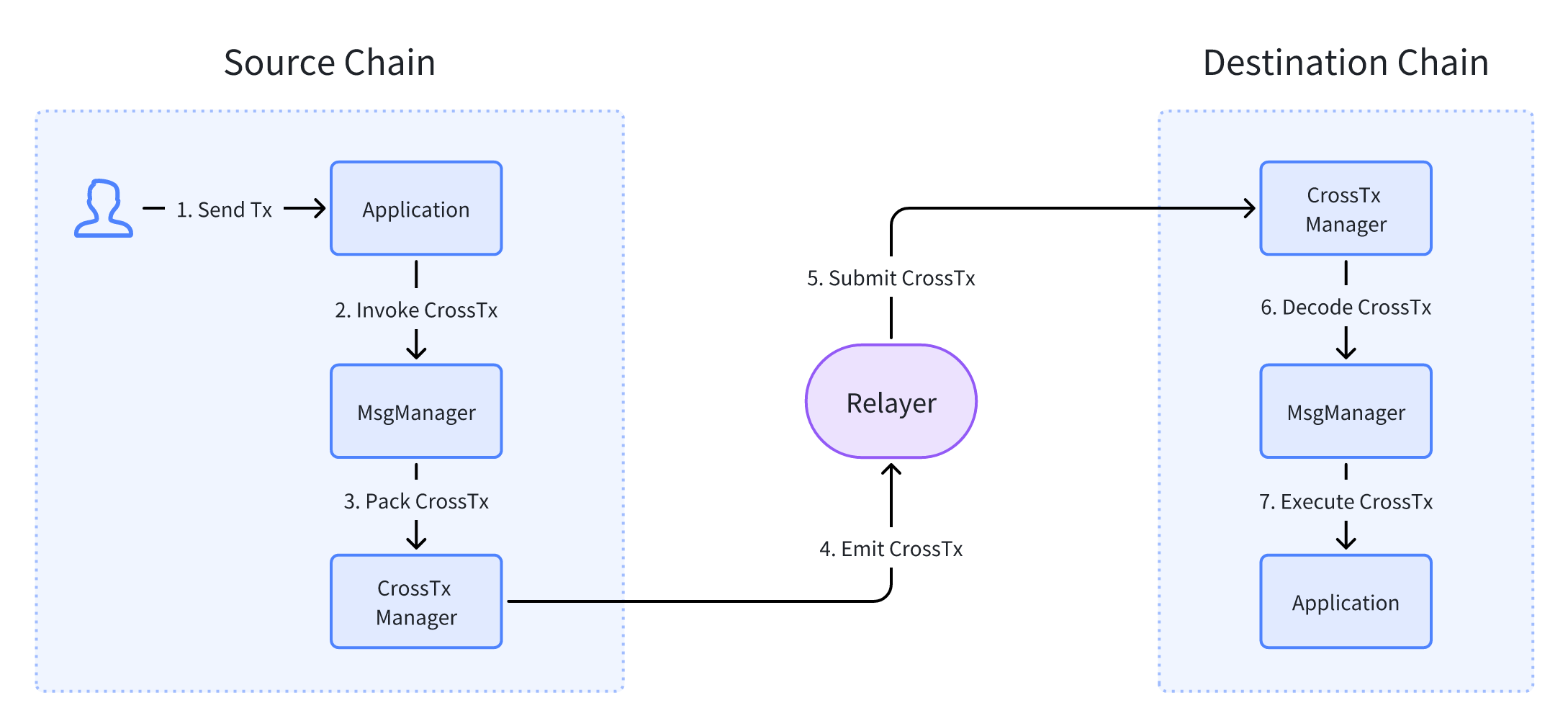
The process of cross-chain messaging is as follows:
- User or application sends a transaction.
- The transaction invokes the cross-chain manager contracts.
- The contracts pack the cross-chain message and emit the cross-chain message event.
- The relayer captures the cross-chain message event, and both services of the relayer send cross-chain message transaction to the destination chain.
- The cross-chain manager contracts on destination chain get the transaction and unpack the cross-chain message.
- The cross-chain manager contracts of the destination chain invoke application contracts and finish the cross-chain message process.
Asset Cross-Chain Process
Cross-chain asset transfers are relatively more complex. To ensure the atomicity of cross-chain asset transfers, the messages for asset cross-chain need to wait for receipts sent by the destination chain. Only upon receiving a successful receipt, the assets from the source chain will be effectively locked. In case of a failed receipt or if the acknowledgment is not received within the timeout, the assets from the source chain will be returned to the user or on-chain application.
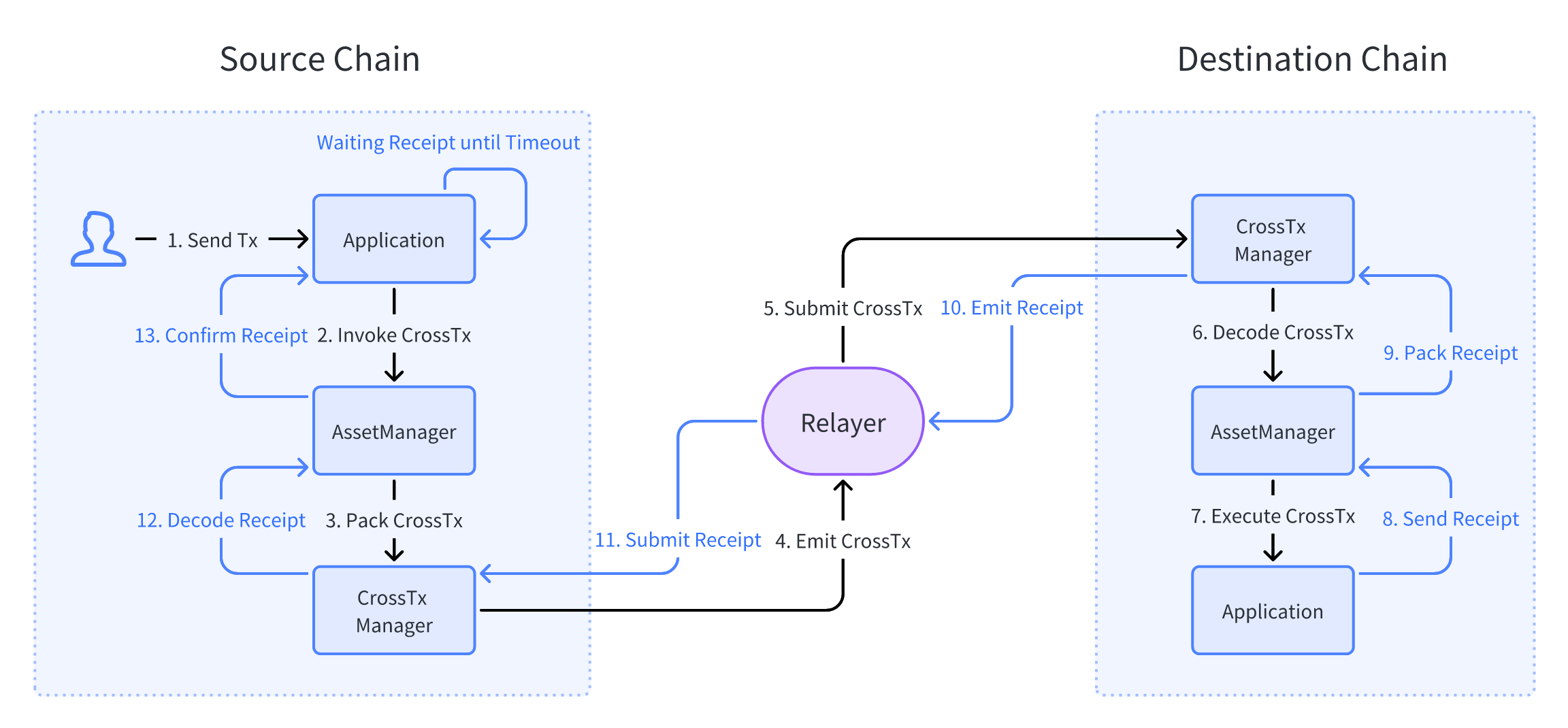
The process of asset cross-chain is as follows:
- User or application sends a transaction.
- The transaction invokes the cross-chain manager contracts.
- The contracts pack the cross-chain asset message and emit the cross-chain message event.
- The relayer captures the cross-chain asset message event, and both services of the relayer send cross-chain asset message transaction to the destination chain.
- The cross-chain manager contracts on destination chain get the transaction and unpack the cross-chain message.
- The cross-chain manager contracts on the destination invoke application contracts.
- If the destination contract execution is successful, a success receipt will be returned; otherwise, a failure receipt will be returned.
- The relayer captures the receipt and returns the receipt to the source chain.
- The source chain contract evaluates the receipt and executes instructions to either lock the assets or return the assets.
Deep in Assets Cross-chain
In cross-chain asset transfers, the most critical aspect to be concerned about is the status of the assets at each stage.
Below is the state diagram of assets in cross-chain asset transfers:
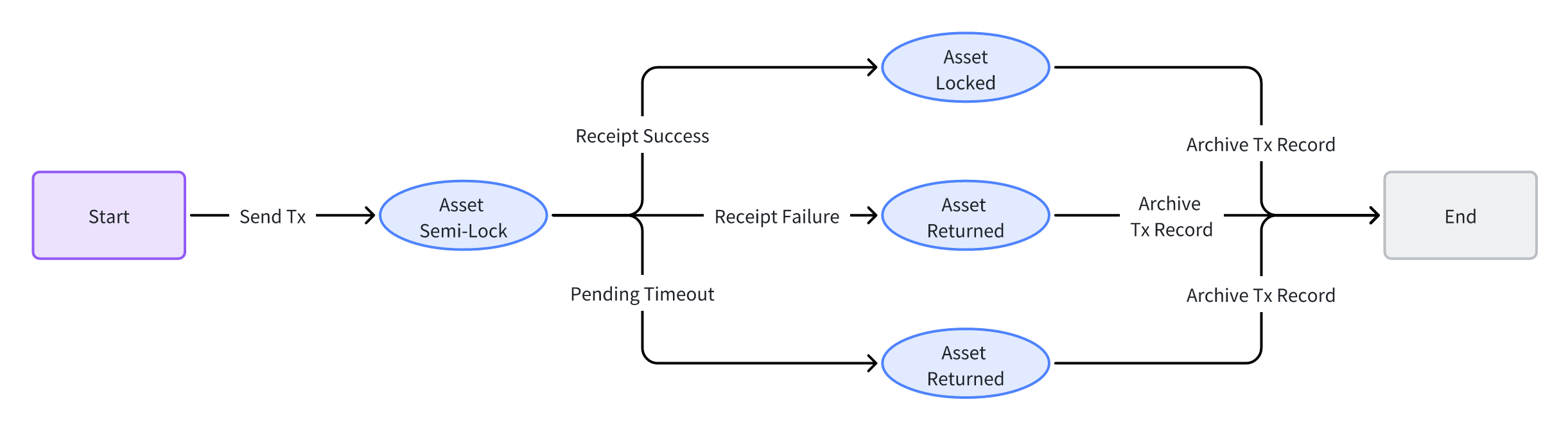
When a user initiates a cross-chain asset transfer, the assets will enter a semi-locked state. In this state, the assets are recorded in Axiomesh’s cross-chain contract but not fully locked. Next steps require waiting for the acknowledgment receipt from the cross-chain message before.
When the source chain receives a success receipt, the assets will be locked on the source chain. If a failure receipt is received, the assets will be returned to the original user or contract.
Axiomesh’s cross-chain system also incorporates a timeout mechanism for transactions. When the assets in a semi-locked state on the source chain do not receive an acknowledgment receipt from the destination chain within a certain time frame, users or on-chain contracts can manually trigger a timeout rollback. This process will return the semi-locked assets back to the original user or contract.